Theme: Reduce and Recycle Waste for Sustainable Waste Management
WASTE RECYCLING CONGRESS 2019
Sydney is one of the world’s most green, global and connected cities. As Australia’s leading global city and the gateway to Asia, Sydney is the destination of choice for International corporations, Business Leaders, Tourists and Students. Sydney provides headquarters for almost 40% of the top 500 Australian corporations. Digital, financial, educational and creative businesses are all thriving in Sydney – supported by our robust economic strategy. Through the City of Sydney’s Sustainable Sydney 2030 program, Sydney is recognized internationally for its outstanding environmental performance and major cultural events, and as a future focused and innovative business Centre. Sydney is also host to one of the largest Chinese New Year Festivals in the world.
Increased globalization and a surge in population and Gross Domestic Product (GDP), among others, have led to an increase in the overall waste volume globally.
According to World Bank in 2012, urban population produced about 1.3 billion tons of Municipal Solid Waste (MSW) which is expected to grow to 2.2 billion tons in 2025. The costs for managing solid waste is expected to increase drastically in lower middle (four times) income countries such as India and Brazil among others and even higher in low-income countries (five times) such as Kenya and Ghana among others. Therefore, the need for solid waste management has increased largely on a global scale.
To increase the recycling across the world, initiatives are being taken by the government agencies of various regions. Market players are taking measures to recycle the E-Waste in order to reduce the pollution and environmental hazards caused by it. In June 2014, Dell, a leading computer manufacturer, launched its first computer made of plastics obtained from recycled electronics. The company has started selling its first computer “the OptiPlex 3030” which is made up of old electronics using closed loop recycling process. Recently, Dell has also started using recycled plastics in its other desktops and monitors. Millions of refrigerators, TV sets and cell phones are replaced with newer versions due to user’s growing inclination towards technologically advanced gadgets. In 2010, US discarded about 258 million units of computers, cell phones, TV sets, and monitors. North America is a leader in exporting E-waste to the developing countries such as China and Australia. This exported E-Waste is then recycled in developing regions which generate revenue for the market.
Segment Overview:
- A number of materials recycled in Singapore in 2007 was 142.3 million metric tons. This is expected to increase to 158.6 million metric tons in 2008 and 244.8 million metric tons in 2013, for a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 9.1%.
- Recycled metals are the largest segment at 76.8 million metric tons in 2007. This should grow to 83.5 million metric tons in 2008 and 123.2 million metric tons in 2013, a CAGR of 8.1%.
- The fastest growing segment is recycled tires and reclaimed rubber; 1.9 million metric tons were recycled in 2007, and an estimated 2.2 million metric tons in 2008. This should reach 4.2 million metric tons in 2013, for a CAGR of 14.0%.
The world recycling market is segmented by recycling source and type. Presently, a market trend is observed in North America that highlights the fact that majority of E-Waste is trashed to developing countries, rather than recycling or reusing the same by the producing country.
Developing countries lead in recycling the E-Waste, a majority of E-Waste is exported to emerging countries by developed countries. Amongst all sources of E-Waste such as IT and telecommunications and consumer electronics, refrigerator sets from household appliances are discarded in highest number as compared to other appliances. The decrease in the life cycle of electronic products viz. computers, laptops, cell phones is generating a large amount of electronic waste in the North American region.
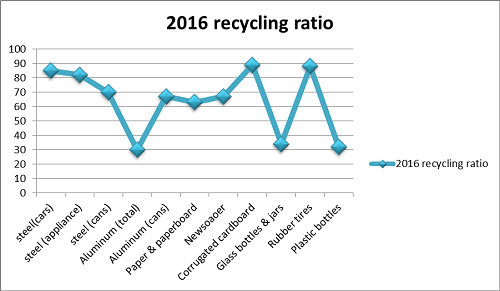
2016 ratio of recycling
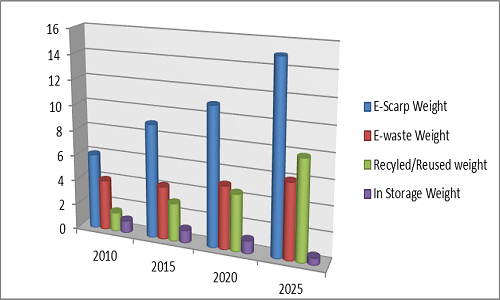
Amount of E-waste recycled /reused and in storage adjusted sales by year, world market: 2010-2025
Plastic packaging recovery and recycling in the Australia
The research methodology used to estimate and forecast the metal recycling market begins with capturing data on key vendor revenues through secondary research. The vendor offerings are also taken into consideration to determine the market segmentation. The bottom-up procedure was employed to arrive at the overall market size of the global metal recycling market from the revenue of the key players in the market. After arriving at the overall market size, the total market was split into several segments and sub segments, which were then verified through primary research by conducting extensive interviews with key people such as CEOs, VPs, directors, and executives. These data triangulation and market breakdown procedures were employed to complete the overall market engineering process and arrive at the exact statistics for all segments and sub segments. The metal recycling market comprises companies such as ArcelorMittal (Luxembourg), Nucor Corporation (U.S.), Commercial Metals Company (U.S.), Sims Metal Management Limited (U.S.), and Aurubis AG (Germany).
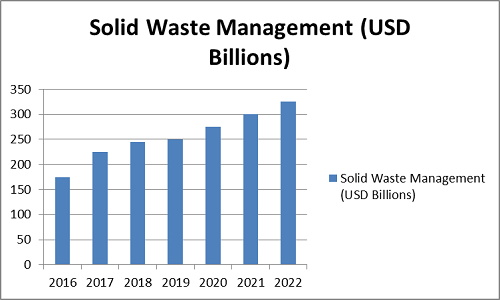
Solid Waste Management report
Conference Highlights
- Environmental Chemistry
- Reduce, Reuse, Recycle and Recovery
- Waste and Biomass Valorization
- Biodiesel and Biofuels
- Bio- Electrochemical Treatment Systems
- Bio- Plastics
- Solid Waste Management
- Renewable Resources
- Waste Water treatments
- Bioremediation
- E-Wastes
- Bio- Energy from Waste
- Sustainable waste Management
- Environmental impact Assessment
- Remote Sensing and Satellite Technology
- Landfills
- Microbial Fuel cell Technology
- Recycling Business
- Waste Treatment Technologies
- Waste Processing Industries
- Pollution and Climate Change
To share your views and research, please click here to register for the Conference.
To Collaborate Scientific Professionals around the World
| Conference Date | October 21-22, 2019 | ||
| Sponsors & Exhibitors |
|
||
| Speaker Opportunity Closed | |||
| Poster Opportunity Closed | Click Here to View | ||
Useful Links
Special Issues
All accepted abstracts will be published in respective Our International Journals.
- Journal of Environmental & Analytical Toxicology
- Journal of Bioremediation & Biodegradation
- Advances in Recycling & Waste Management
Abstracts will be provided with Digital Object Identifier by











